“Understanding and Managing High Blood Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide”
High blood pressure, often known as hypertension, silently affects millions worldwide, posing significant health risks if left unchecked. This prevalent condition demands attention, understanding, and proactive management for a healthier life. Let’s navigate the complexities of high blood pressure, demystifying its causes, implications, and strategies for effective management.
Huge Online Sale (Now Up To 70% Off) Buy High Blood Pressure Relief At The Lowest Price Here
What is High Blood Pressure?

High blood pressure occurs when the force of blood against the artery walls remains consistently high. This strain on the arteries can lead to severe health complications, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems. The tricky part? Often, there are no noticeable symptoms, earning it the moniker of a “silent killer.”
Understanding the Causes
Factors contributing to high blood pressure include an unhealthy diet high in sodium, inadequate physical activity, excessive alcohol consumption, and smoking. Additionally, stress and genetics play significant roles in elevating blood pressure levels.
(Exclusive Deal) Get A Huge Discount By Purchasing High Blood Pressure Relief From The Official Website Here
How do I know if I have blood pressure?
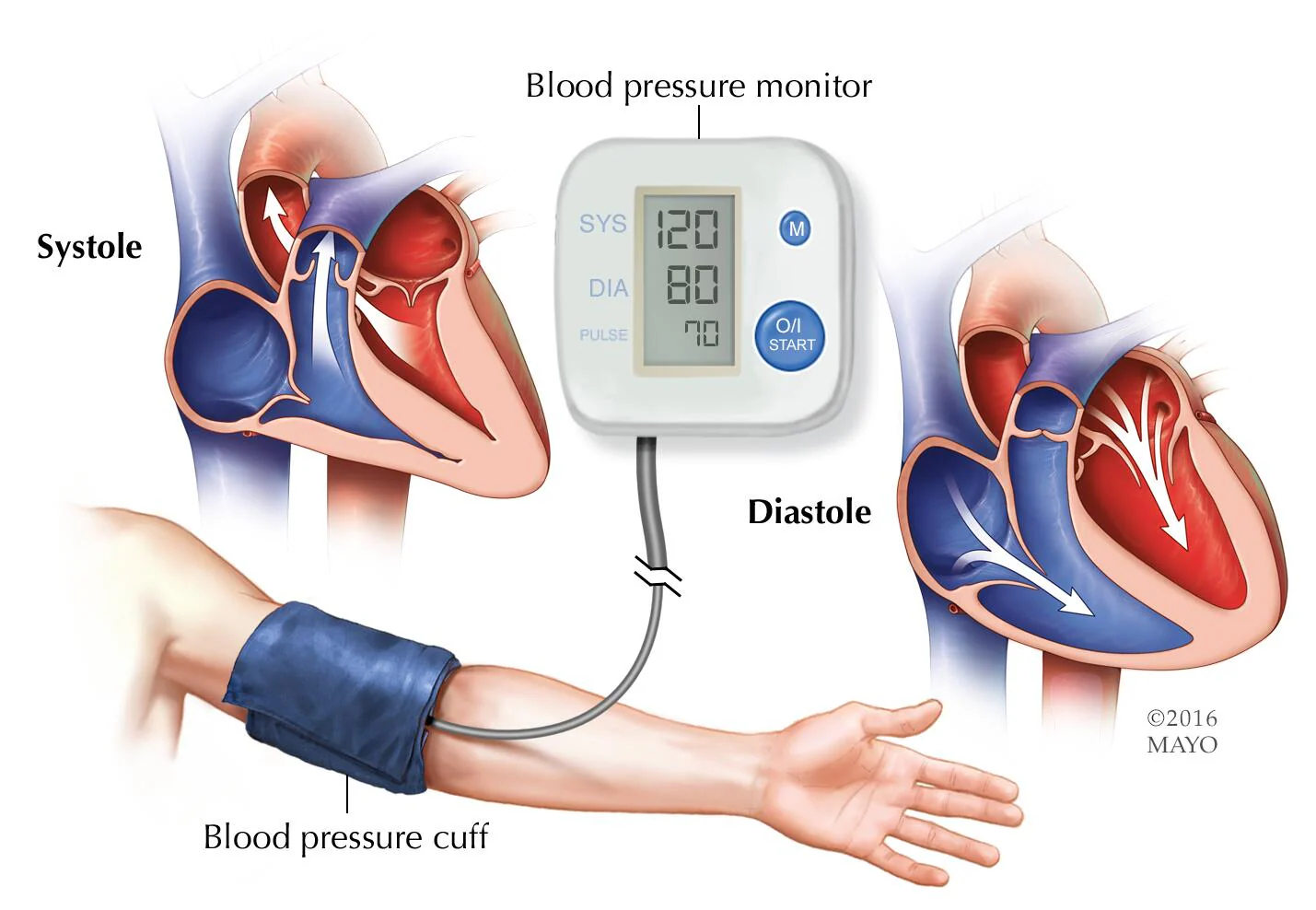
The essential gateway to understanding your blood pressure levels rests in the act of getting them checked. While feeling healthy might suggest everything’s fine, the truth about high blood pressure lies in the numbers revealed during regular healthcare checkups. This seemingly routine check can be a life-saving endeavor. High blood pressure often lurks without noticeable symptoms, underscoring the critical importance of these routine appointments. If your readings surpass the normal range, your healthcare provider becomes a vital ally, offering tailored recommendations—be it lifestyle adjustments, dietary changes, increased physical activity, or even medication—to effectively lower and manage those numbers.
(Limited-Time Offer] We Found The Lowest Discounted Price For High Blood Pressure Relief Right Here
What is considered high blood pressure?
Absolutely! This is a regional aspect that speaks to how different parts of the world define high blood pressure. For instance, in the United States, healthcare providers define high blood pressure, or hypertension, as having a systolic blood pressure of at least 130 mmHg or a diastolic blood pressure of at least 80 mmHg. In contrast, across Europe, healthcare practitioners tend to diagnose hypertension when the systolic blood pressure hits at least 140 mmHg or the diastolic blood pressure reaches at least 90 mmHg. These slight differences highlight how interpretations can vary based on geography, influencing how healthcare professionals approach diagnosing and managing high blood pressure.
How common is high blood pressure?
High blood pressure casts a prevalent shadow across communities, affecting nearly half of the adult population in the United States—equivalent to approximately 116 million individuals. Within this substantial number, a staggering 37 million individuals grapple with blood pressure levels reaching or surpassing 140/90 mmHg. The gravity of this condition manifests in its dire consequences, as evidenced by its involvement in over 670,000 deaths in the U.S. in the year 2020 alone. Globally, the World Health Organization’s estimations paint a grave picture, highlighting that over 1.2 billion individuals between the ages of 30 to 79 battle hypertension. Alarmingly, two out of three affected individuals find themselves in low- or middle-income countries, emphasizing the pervasive nature of this health concern, particularly in regions with fewer resources for comprehensive healthcare.
High Blood Pressure Relief Official Website For Order Placement: Click Here To Order Now
Symptoms and Causes
Detecting high blood pressure isn’t always straightforward since it often lurks without noticeable signals, earning its ominous nickname as the ‘silent killer.’ It’s astonishing that many individuals could unknowingly live with high blood pressure for years, as the World Health Organization estimates nearly half of adults with hypertension are unaware of their condition.
However, when blood pressure reaches 180/120 mmHg or higher, it can manifest in troubling symptoms like throbbing headaches, irregular heartbeats, or even nosebleeds. At this stage, it’s considered a hypertensive crisis requiring immediate medical attention.
Healthcare providers typically classify high blood pressure into two main types:
Primary hypertension, which accounts for approximately 90% of adult cases in the U.S., often results from age-related changes and lifestyle factors such as insufficient physical activity.
Secondary hypertension, on the other hand, stems from different underlying medical conditions or sometimes arises as a consequence of certain medications.
Interestingly, both primary and secondary high blood pressure can coincide. For instance, a new medical condition might exacerbate an already elevated blood pressure.
Special Promo Offer *Now On Sale* Get High Blood Pressure Relief At A Discounted Price Today!
Additionally, there are specific types of high blood pressure that vary in different situations:
- White coat hypertension: Blood pressure reads higher in a medical setting but remains normal in a familiar environment like home.
- Masked hypertension: Opposite to the above, blood pressure appears normal in medical settings but spikes when measured at home.
- Sustained hypertension: Blood pressure remains consistently high in both medical and home settings.
- Nocturnal hypertension: Blood pressure rises during sleep, indicating a unique pattern.
These variations highlight the complexity of diagnosing high blood pressure and emphasize the importance of considering different scenarios and environments when evaluating one’s blood pressure readings.
Blood pressure categories
In 2017, the American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association set out revised guidelines, becoming the gold standard for diagnosing and managing high blood pressure in the U.S. These guidelines provide a clear framework, categorizing blood pressure readings into four distinct stages, each delineating the level of severity and necessary interventions.
Let’s break it down:
- Normal blood pressure: Your blood pressure reading falls below 120 mmHg for the top number (systolic BP) and below 80 mmHg for the bottom number (diastolic BP). This range is considered the optimal benchmark for a healthy blood pressure reading.
- Elevated blood pressure: It lands between 120 to 129 mmHg for the top number (systolic BP) and remains below 80 mmHg for the bottom number (diastolic BP), signaling a borderline reading that warrants attention and proactive lifestyle changes.
- Stage 1 hypertension: This stage encompasses readings ranging from 130 to 139 mmHg for the top number (systolic BP) or 80 to 89 mmHg for the bottom number (diastolic BP), indicating the onset of high blood pressure.
- Stage 2 hypertension: Blood pressure readings at 140 mmHg or higher for the top number (systolic BP) or 90 mmHg or higher for the bottom number (diastolic BP) fall into this category, signaling a more severe and uncontrolled level of high blood pressure.
In the U.S., a diagnosis of high blood pressure aligns with having a top number of at least 130 and/or a bottom number of at least 80. Understanding these guidelines helps healthcare providers accurately diagnose and initiate appropriate interventions tailored to each individual’s blood pressure readings.
(Huge Savings Today) Click Here To Order High Blood Pressure Relief At The Lowest Price While Supplies Last
Management and Treatment
What are the treatments for high blood pressure?
Addressing high blood pressure encompasses a spectrum of treatments that span lifestyle adjustments and medicinal interventions. Tailored recommendations from healthcare providers hinge on a comprehensive assessment, considering not only your blood pressure readings but also delving into the root causes of your elevated numbers and any underlying health conditions. This personalized approach ensures that the recommended treatment regimen aligns precisely with your unique health profile, optimizing the effectiveness of interventions and promoting long-term management of high blood pressure.
Lifestyle changes to lower your blood pressure
Contemplating ways to naturally reduce your blood pressure? The answer is a resounding ‘yes.’ In many cases, lifestyle changes can significantly impact blood pressure levels without the need for medications, especially if you find yourself dealing with elevated blood pressure or stage 1 hypertension.
There’s a multitude of proven methods to naturally lower your blood pressure, starting with a focus on your lifestyle:
Maintaining a healthy weight is key. Your healthcare provider can guide you toward a target range suitable for your body.
Adopting a wholesome diet, such as the DASH diet, can work wonders. This eating plan emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy, promoting heart-healthy choices.
Taming your salt intake is crucial. Ideally, aim to limit sodium consumption to no more than 1,500 milligrams per day. If this seems daunting initially, start by gradually reducing your daily intake by at least 1,000 milligrams.
Prioritize potassium-rich foods, aiming for 3,500 to 5,000 milligrams daily, preferably through natural sources like bananas, avocados, and potatoes with the skin.
Incorporate exercise into your routine. Seek guidance from your healthcare provider to kickstart your fitness journey, gradually working up to 150 minutes of aerobic exercise weekly, complemented by resistance training.
Balancing your enjoyment of alcoholic beverages with your health objectives is a mindful endeavor. Choosing to partake in alcohol should align with your wellness aspirations, including maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.
Occasionally, healthcare providers may recommend lifestyle changes in conjunction with medications to effectively manage blood pressure.
Regarding medications designed to lower blood pressure, there are four primary classes of ‘first-line’ drugs commonly prescribed:
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors work by hindering the production of angiotensin II, a hormone involved in blood pressure regulation. By preventing its narrowing effect on blood vessels, these medications aid in blood pressure management.
Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) function similarly to ACE inhibitors by obstructing the action of angiotensin II on blood vessels, maintaining their dilation and reducing blood pressure.
Calcium channel blockers relax heart and blood vessel muscles by preventing calcium from entering these cells, promoting vessel relaxation and lower blood pressure.
Diuretics, or ‘water pills,’ assist in flushing out excess sodium and fluids from the body, effectively reducing blood volume and aiding blood pressure control.
Sometimes, combining other medications with these ‘first-line’ drugs helps in better blood pressure management.
Discussing possible side effects with your provider is crucial. If you encounter any concerns, don’t hesitate to reach out; altering dosage or switching medications might be an option. Avoid discontinuing medications without consulting your provider.
During pregnancy, some medications pose risks, so informing your provider about pregnancy or potential conception is essential.”
Remember, individual responses to medications may vary, and open communication with your healthcare provider is key to finding the most suitable approach for managing blood pressure.
(Limited Time Offer) Click Here To Buy High Blood Pressure Relief At The Lowest Price Today Before Stock Ends!
The Implications of Untreated High Blood Pressure
Lifestyle Modifications
Embracing a healthy lifestyle is pivotal in managing high blood pressure. This involves adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while reducing sodium intake. Regular physical activity, stress reduction techniques, and quitting smoking also play crucial roles.
Medication and Monitoring
In some cases, medication prescribed by healthcare professionals might be necessary to manage high blood pressure effectively. Regular monitoring of blood pressure levels is essential to track progress and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
Conclusion
High blood pressure is a prevalent and potentially life-threatening condition, but it’s manageable. Empowerment lies in understanding its nuances, making informed lifestyle choices, seeking professional guidance, and consistently monitoring and managing this condition.
Taking charge of your health starts with understanding high blood pressure and its implications. By adopting a proactive approach and making positive lifestyle changes, you pave the way toward a healthier and more fulfilling life.
To Enjoy The Benefits Of High Blood Pressure Relief, Click Here To Order Your Supply Now!